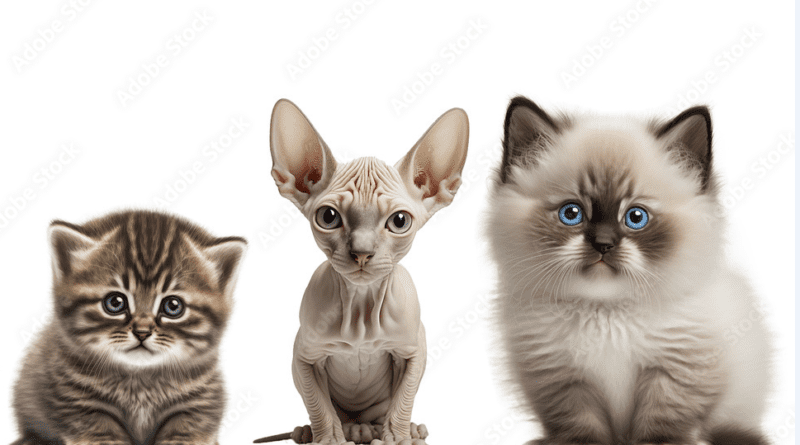
Classification of Cat Breeds
Cats are some of the most diverse domestic animals, with over 70 recognized breeds differing in appearance, personality, and origin. This diversity creates the need for a classification system to identify breeds accurately. While breed identification can be based on physical traits, personality, or geographic origin, four main factors are most commonly used: coat length, geographic origin, temperament, and coat patterns. These classifications not only help distinguish cat breeds but also highlight the uniqueness of each one.
Several breed registries, including the Cat Fanciers’ Association (CFA), The International Cat Association (TICA), and Fédération Internationale Féline (FIFe), standardize these characteristics. Depending on the registry, they recognize anywhere between 45 to 73 distinct breeds. Let’s explore how these categories are organized.
Coat Length Classification
Coat length is one of the easiest ways to classify cats. Their coats can be short, long, or hairless, and each type comes with its own unique appeal. Let’s examine some popular breeds within each category.
Short-Haired Cats
Short-haired breeds are known for their easy maintenance, requiring less grooming than long-haired varieties.
- British Shorthair: This breed is famous for its dense, plush coat and round face. British Shorthairs are calm, affectionate, and often favored by families.
- Siamese: With their sleek bodies and piercing blue eyes, Siamese cats are iconic. They are also known for their vocal and affectionate personalities.
Long-Haired Cats
Long-haired breeds are admired for their luxurious coats, but they need regular grooming to prevent matting.
- Persian: One of the oldest and most recognizable breeds, the Persian boasts a thick, flowing coat. Their docile nature makes them ideal companions.
- Maine Coon: Known for their large size and shaggy coat, Maine Coons are playful and dog-like, making them a popular choice for families.
Hairless Cats
Hairless cats stand out due to their lack of fur. Despite this, they still require regular skincare.
- Sphynx: Famous for its warm, soft skin, the Sphynx is beloved for its affectionate and friendly nature, appealing to those who prefer unique pets.
Geographic Origin Classification
Geographic origin is another common method for classifying cats. Different regions of the world have produced distinct breeds with unique traits shaped by their environments.
Asian Breeds
Asian cats tend to have sleek bodies and an elegant appearance.
- Siamese: Originating from Thailand (formerly Siam), Siamese cats are known not just for their appearance but also for their sociable and vocal nature.
- Burmese: These muscular cats come from Southeast Asia. Their sleek coats and affectionate personalities make them loyal companions.
European Breeds
European breeds often developed thick coats to survive colder climates.
- British Shorthair: Native to the UK, this breed’s dense coat helps it stay warm in cool climates.
- Norwegian Forest Cat: Hailing from Norway, this breed features a thick, water-resistant coat, perfect for harsh winters.
North American Breeds
North America has produced its own distinct breeds, well adapted to various climates.
- Maine Coon: Native to the northeastern United States, Maine Coons are large with thick coats to endure cold weather.
- Sphynx: This hairless breed originated in Canada during the 1960s. Despite lacking fur, Sphynx cats are playful and affectionate, known for their unique appearance.
Temperament-Based Classification
Personality plays a significant role in how cat breeds are classified. Although individual cats have unique traits, certain temperamental characteristics are common to specific breeds.
Affectionate Breeds
Some breeds are known for their desire to be close to their owners and their social nature.
- Ragdoll: Ragdolls are known for their relaxed and calm temperament. They enjoy being held and often go limp when picked up, hence the name.
- Siamese: These cats are highly vocal and affectionate, forming strong bonds with their owners and craving attention.
Independent Breeds
Some breeds prefer independence, though they can still develop strong attachments to their families.
- Russian Blue: Known for their quiet and reserved nature, Russian Blues thrive in peaceful environments.
- Scottish Fold: Famous for their unique folded ears, Scottish Folds tend to be more independent but can also be affectionate on their terms.
Playful and Energetic Breeds
Certain breeds are full of energy, making them ideal for active households.
- Bengal: With its wild-looking spots and energetic personality, the Bengal loves to explore, jump, and play.
- Abyssinian: These athletic cats are curious and love engaging in constant activities, making them one of the most playful breeds.
Coat Pattern Classification
Cats can also be classified by their coat patterns, which vary widely, from solid colors to intricate designs.
Solid Colors
Some cats have uniform, solid-colored coats that stand out for their simplicity.
- Russian Blue: This breed’s shimmering blue-gray coat is a perfect example of a stunning solid color.
- Bombay: With its sleek black coat and golden eyes, the Bombay cat is often likened to a mini panther.
Tabby Patterns
Tabby patterns include stripes, spots, and swirls, seen in various breeds.
- Maine Coon: Many Maine Coons feature the classic tabby pattern, which complements their rugged, wild appearance.
- American Shorthair: This breed often showcases the iconic tabby markings, making it highly recognizable.
Color-Point Patterns
Some cats have color-point patterns, where their face, ears, paws, and tail are darker than the rest of their body.
- Siamese: This breed is known for its striking color-point pattern, with dark extremities contrasting a lighter body.
- Birman: Similar to Siamese cats, Birmans have color-point coats but often display white “gloves” on their paws.
Conclusion
Classifying cats based on coat length, origin, temperament, and patterns offers a comprehensive way to appreciate the feline world’s variety. Whether you’re drawn to the affectionate Siamese, independent Russian Blue, or playful Bengal, each breed has unique traits that set it apart. Registries like CFA, TICA, and FIFe ensure these characteristics are maintained, preserving the beauty and diversity of cat breeds for future generations.