The Lifespan and Health of Domestic Cats
The lifespan of pet cats has significantly increased over the past few decades. Recognizing the factors contributing to this improvement helps cat owners ensure their feline companions live long, healthy lives.
Historical Lifespan Trends
In the early 1980s, the average lifespan of domestic cats was around seven years. By 1995, this average rose to 9.4 years. As of 2014 and continuing into 2023, the average lifespan has reached about 13 years. Remarkably, some cats have been reported to live into their 30s, with the oldest known cat reaching an impressive age of 38. These trends reflect positive changes in feline health and care.
The Role of Neutering
Neutering plays a crucial role in extending a cat’s life. Research indicates that castrated male cats live twice as long as their intact counterparts. Likewise, spayed female cats enjoy a lifespan that is 62% longer than those that remain intact.
Health Benefits of Neutering
Neutering not only extends a cat’s life but also offers significant health benefits. For instance, spaying and neutering lower the risk of reproductive-related diseases and cancers, such as mammary tumors and testicular cancer. Additionally, neutering can prevent mating-related behaviors like yowling, roaming, and aggression.
Potential Drawbacks
However, neutering can impact metabolism, slowing it down and potentially leading to weight gain. Increased food intake in neutered cats may further contribute to obesity if not managed properly. Cat owners should monitor their pets’ diets and activity levels after neutering to maintain a healthy weight.
Genetic Disorders in Cats
Cats can suffer from various heritable genetic disorders. Scientists have identified around 250 genetic conditions in felines, many resembling disorders found in humans. These can include conditions such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, which affects the heart, and polycystic kidney disease.
Diagnosing Genetic Conditions
The metabolic similarities between mammals enable veterinarians to diagnose these feline diseases using genetic tests originally developed for humans. These tests assist in identifying and managing hereditary issues in cats. Early detection through genetic testing can lead to more effective treatment options and enhance the overall quality of life for affected cats.
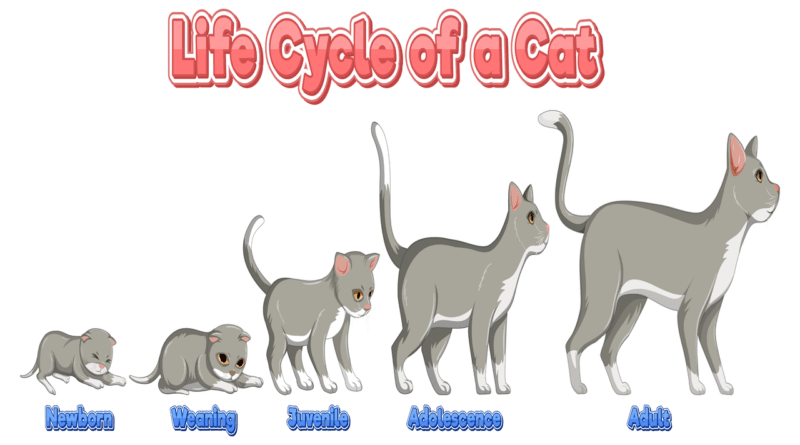
The Four Life Stages of a Cat
The awareness of the life stages of cats helps owners provide appropriate care at each phase. Cats generally progress through four stages: kittens, young adults, mature adults, and old ones. Each stage requires special attention to specific health and behavioral areas.
Kittens (Birth up to 1 Year)
Kittens are known for their high play drive. This stage is ideal for gradual positive introductions to people and other pets. It is also crucial for helping kittens become comfortable with nail trims, tooth and coat brushing, their cat carrier, and veterinary visits.
Young Adults (1 Year – 6 Years)
During this stage, inter-cat aggression may develop alongside sexual maturity. Owners should encourage appropriate play to manage aggression and foster healthy behaviors.
Mature Adults (7 – 10 Years)
As cats enter this stage, their play activity decreases, and they may gain weight. Many owners mistakenly assume their mature cats remain young and healthy, but significant changes can occur. Regular veterinary check-ups become increasingly important to keep them healthy and prevent diseases.
OLd Cats (Over 10 Years)
The human equivalent at the beginning of this life stage is about 60 years. Senior cats may exhibit behavioral changes, such as increased vocalization or altered litter box habits. They should visit the veterinarian at least every six months, as early detection of potential health issues can lead to better outcomes and reduce treatment costs.
Understanding the factors influencing the lifespan and health of cats empowers owners to make informed decisions. Regular veterinary check-ups, a balanced diet, and proper care practices help ensure that cats lead long, healthy, and fulfilling lives. By being proactive about their health, cat owners can enjoy many happy years with their feline companions.